Tài liệu về RAG Prompting với LangChain - Hướng dẫn chi tiết về việc xây dựng ứng dụng RAG sử dụng LangChain
Documents RAG-Prompting-and-LangChain
Documents_RAG-Prompting-and-LangChainh1
I. Giới thiệuh1
LangChain là một framework được thiết kếchuyên biệt cho việc triển khai LLMs trong các ứng dụng thực tế. LangChain hỗ trợ các công cụ và thư viện mạnh mẽ cho phép các nhà phát triển dễdàng tích hợp các mô hình ngôn ngữlớn với các ứng dụng của họ, từ các Chatbot thông minh cho đến các hệ thống phân tích dữ liệu phức tạp.
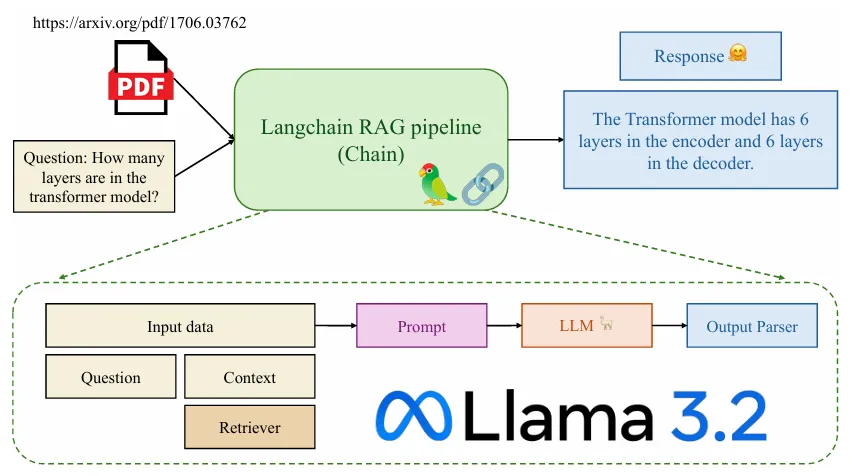
Hình 1: Minh họa ứng dụng hỏi đáp nội dung file pdf sửdụng LangChain. (https://arxiv.org/pdf/1706.03762)
Trong bài viết này, chúng ta sẽ xây dựng một ứng dụng về RAG (Retrieval Augmented Gener-ation) trảlời các câu hỏi học thuật tận dụng nguồn tài liệu là các bài báo khoa học mà ta thu thập được (dưới dạng file pdf), sửdụng thư viện LangChain. Tổng quan, pipeline của project như sau:
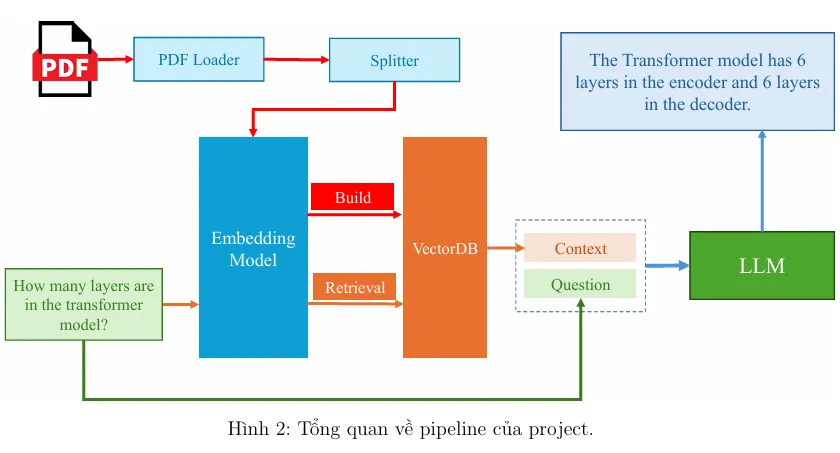
Hình 2: Tổng quan về pipeline của project.
Theo đó:
- Từ danh sách các bài báo khoa học, ta tách thành các văn bản nhỏ. Từ đó, xây dựng một
hệ cơ sở dữ liệu vector với một embedding model.
- Bên cạnh câu hỏi đầu vào (question), ta truy vấn các mẫu văn bản có liên quan đến đến
câu hỏi, dùng làm ngữcảnh (context) trong câu prompt. Đây là nguồn thông tin mà LLMs
có thể dựa vào đểtrảlời câu hỏi.
- Đưa câu prompt vào mô hình (question và context) đểnhận câu trảlời từmô hình.
II. Cài đặt chương trìnhh1
Trong phần này, chúng ta sẽtiến hành cài đặt nội dung của project. Mã nguồn được xây dựng trên hệđiều hành Ubuntu với GPU 24GB. Các bước thực hiện như sau:
II.1. Tổ chức thư mục codeh2
Để mã nguồn trở nên rõ ràng nhằm phục vụ cho mục đích đọc hiểu code, chúng ta sẽtổchức thư mục như sau:
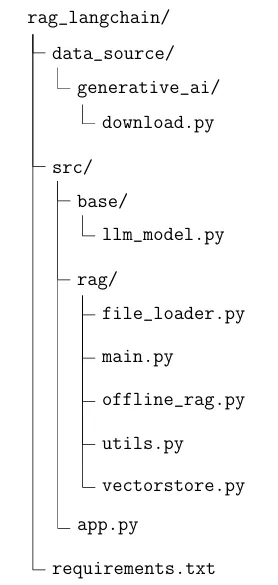
Tổng quan, chúng ta sẽcó thư mục chứa mã nguồn có tên rag_langchain (các bạn hoàn toàn có thể sửdụng tên gọi khác). Bên trong sẽcó các thư mục con và các file với ý nghĩa như sau:
- data_source/: Thư mục dùng đểlưu trữcác tài liệu phục vụcho việc xây dựng hệcơ sở dữliệu vector.
- data_source/generative_ai/download.py: File code dùng đểtải tựđộng một sốcác bài báo khoa học dưới dạng file pdf.
- src/base/llm_model: File code dùng đểkhai báo hàm khởi tạo mô hình ngôn ngữlớn.
- src/rag/: Thư mục dùng đểlưu trữcác code liên quan đến xây dựng RAG, bao gồm:
- src/rag/file_loader.py: File code dùng đểkhai báo các hàm load file pdf (vì tài liệu của chúng ta thu thập thuộc file pdf).
- src/rag/main.py: File code dùng đểkhai báo hàm khởi tạo chains.
- src/rag/offline_rag.py: File code dùng đểkhai báo PromptTemplate.
- src/rag/utils.py: File code dùng đểkhai báo hàm tách câu trảlời từmodel.
- src/rag/vectorstore.py: File code dùng đểkhai báo hàm khởi tạo hệcơ sởdữliệu vector.
- src/app.py: File code dùng đểkhởi tạo API.
- requirements.txt: File code dùng đểkhai báo các thư viện cần thiết đểsửdụng source code.
II.2. Cập nhật file requirements.txth2
Để bắt đầu, chúng ta sẽ liệt kê các gói thư viện cần thiết để chạy được chương trình này. Các bạn hãy cập nhật file requirements.txt với nội dung sau:
1 torch ==2.2.2
2 transformers ==4.39.3
3 accelerate ==0.28.0
4 bitsandbytes ==0.42.0
5 huggingface -hub==0.22.2
6 langchain ==0.1.14
7 langchain -core ==0.1.43
8 langchain -community ==0.0.31
9 pypdf ==4.2.0
10 sentence - transformers ==2.6.1
11 beautifulsoup4 ==4.12.3
12 langserve[all]
13 chromadb ==0.4.24
14 langchain -chroma ==0.1.0
15 faiss -cpu==1.8.0
16 rapidocr -onnxruntime ==1.3.16
17 unstructured ==0.13.2
18 fastapi ==0.110.1
19 uvicorn ==0.29.0
II.3. Cập nhật file data_source/generative_ai/download.- py
Đểtải một vài các bài báo khoa học làm dữliệu cho hệcơ sởdữliệu vector, chúng ta sẽxây dựng một đoạn code tải tựđộng các bài báo. Nội dung như sau:
1 import os
2 import wget
4
AI VIETNAM (AIO2024) aivietnam.edu.vn
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29 ]
30
31 def
32
33
34 for
35
36
4 file_links = [
{
“title”: “Attention Is All You Need”,
“url”: “https :// arxiv.org/pdf/1706.03762”
},
{
“title”: “BERT - Pre -training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for
Language Understanding”,
“url”: “https :// arxiv.org/pdf/1810.04805”
},
{
“title”: “Chain -of -Thought Prompting Elicits Reasoning in Large
Language Models”,
“url”: “https :// arxiv.org/pdf/2201.11903”
},
{
“title”: “Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models”,
“url”: “https :// arxiv.org/pdf/2006.11239”
},
{
“title”: “Instruction Tuning for Large Language Models - A Survey”,
“url”: “https :// arxiv.org/pdf/2308.10792”
},
{
“title”: “Llama 2- Open Foundation and Fine -Tuned Chat Models”,
“url”: “https :// arxiv.org/pdf/2307.09288”
}
is_exist(file_link):
return os.path.exists(f”./{file_link[’title ’]}.pdf”)
file_link in file_links:
if not is_exist(file_link):
wget.download(file_link[“url”], out=f”./{file_link[’title ’]}.pdf”)
3
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
Trong file code trên, chúng ta cung cấp một list các đường dẫn bài báo. Từđó, sửdụng wget đểtải về. Các bài báo sẽđược lưu ngay tại vịtrí của file code. Vì mục đích demo, chúng ta sẽchỉtải một sốlượng nhỏcác paper. Các bạn có thểtựthêm vào nhiều paper khác đểtest.
5
AI VIETNAM (AIO2024) aivietnam.edu.vn
Hình 3: Minh họa danh sách các file bài báo khoa học sau khi được tải về.
II.4. Cập nhật file src/base/llm_model.py
Tại file này, ta khai báo hàm get_hf_model(), dùng đểthực hiện tải và gọi pre-trained LLM từHuggingFace vềmáy. Đồng thời, ta áp dụng kỹthuật quantization lên model đểthực hiện inference trên GPU thấp. Nội dung file như sau:
12 )
13
14 def
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
1 import torch
2 from transformers import BitsAndBytesConfig
3 from transformers
import AutoTokenizer , AutoModelForCausalLM , pipeline 4 from langchain.llms. huggingface_pipeline import HuggingFacePipeline
7 nf4_config = BitsAndBytesConfig (
load_in_4bit=True ,
bnb_4bit_quant_type =“nf4”,
bnb_4bit_use_double_quant =True ,
bnb_4bit_compute_dtype =torch.bfloat16
get_hf_llm(model_name: str = “meta -llama/Llama -3.2-3B -Instruct”, max_new_token = 1024 ,
** kwargs):
model = AutoModelForCausalLM .from_pretrained (
model_name ,
quantization_config =nf4_config ,
low_cpu_mem_usage =True
)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer. from_pretrained (model_name)
5
6
8
9
10
11
6
AI VIETNAM (AIO2024) aivietnam.edu.vn
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
model_pipeline = pipeline(
“text -generation”,
model=model ,
tokenizer=tokenizer ,
max_new_tokens =max_new_token ,
pad_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id , device_map=“auto”
)
llm = HuggingFacePipeline (
pipeline=model_pipeline ,
model_kwargs=kwargs
)
return llm
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
Trong project này, mô hình LLM mà chúng ta sửdụng là mô hình Llama 3.2 3B được huấn luyện trên dữliệu instruction. Các bạn có thểthay thếbằng mô hình khác có cấu hình tương tự.
II.5. Cập nhật file src/rag/file_loader.py
17 def
18
19
21
22
23
24
25
26
28
29
30
31
32
1 from typing import Union , List , Literal
2 import glob
3 from tqdm import tqdm
4 import multiprocessing
5 from langchain_community . document_loaders import PyPDFLoader
6 from langchain_text_splitters import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
8 def remove_non_utf8_characters (text):
return ’’.join(char for char in text if ord(char) < 128)
load_pdf(pdf_file):
docs = PyPDFLoader(pdf_file , extract_images=True).load ()
for doc in docs:
doc.page_content = remove_non_utf8_characters (doc.page_content)
return docs
get_num_cpu ():
return multiprocessing.cpu_count ()
20 class BaseLoader:
def init(self) -> None:
self.num_processes = get_num_cpu ()
def call(self , files: List[str], ** kwargs):
pass
27 class PDFLoader(BaseLoader):
def init(self) -> None:
super ().init ()
def call(self , pdf_files: List[str], ** kwargs):
num_processes = min(self.num_processes , kwargs[“workers”])
7
9
10
11 def
12
13
14
15
16
7
AI VIETNAM (AIO2024) aivietnam.edu.vn
33 with multiprocessing .Pool(processes=num_processes) as pool:
34 doc_loaded = []
35 total_files = len(pdf_files)
36
with tqdm(total=total_files , desc=“Loading PDFs”, unit=“file”) as pbar:
37 for result in pool.imap_unordered (load_pdf , pdf_files): 38 doc_loaded.extend(result)
39
pbar.update(1) 40 return doc_loaded
41
42 class TextSplitter:
43
def init(self , 44 separators: List[str] = [’\n\n’, ’\n’, ’ ’, ’’],
45 chunk_size: int = 300 ,
46 chunk_overlap: int = 0
47 ) -> None:
48
49 self.splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter (
50 separators=separators ,
51
chunk_size=chunk_size , 52 chunk_overlap=chunk_overlap ,
53 )
54 def call(self , documents):
55 return self.splitter.split_documents (documents)
56
57 class Loader:
58 def
init(self , 59 file_type: str = Literal[“pdf”],
60 split_kwargs: dict = {
61 “chunk_size”: 300 ,
62
“chunk_overlap”: 0} 63 ) -> None:
64 assert file_type in [“pdf”], “file_type must be pdf”
65
self.file_type = file_type 66 if file_type == “pdf”:
67 self.doc_loader = PDFLoader ()
68 else:
69
raise ValueError(“file_type must be pdf”) 70
71 self.doc_spltter = TextSplitter (** split_kwargs)
72
73
def load(self , pdf_files: Union[str , List[str]], workers: int = 1): 74 if isinstance(pdf_files , str):
75 pdf_files = [pdf_files]
76 doc_loaded = self.doc_loader(pdf_files , workers=workers)
77
doc_split = self.doc_spltter(doc_loaded) 78 return doc_split
79
80 def load_dir(self , dir_path: str , workers: int = 1):
81 if self.file_type == “pdf”:
82 files = glob.glob(f”{dir_path}/*. pdf”)
83 assert len(files) > 0, f”No {self.file_type} files found in { dir_path}”
84 else:
85 raise ValueError(“file_type must be pdf”)
8
AI VIETNAM (AIO2024) aivietnam.edu.vn
86
return self.load(files , workers=workers)
II.6. Cập nhật file src/rag/vectorstore.py
Tại file này, ta định nghĩa một class đểkhởi tạo hệcơ sởdữliệu vector. Trong project này, chúng ta sẽsửdụng Chroma. Vềviệc tìm kiếm tài liệu tương đồng, ta sửdụng FAISS. Như vậy, nội dung của file như sau:
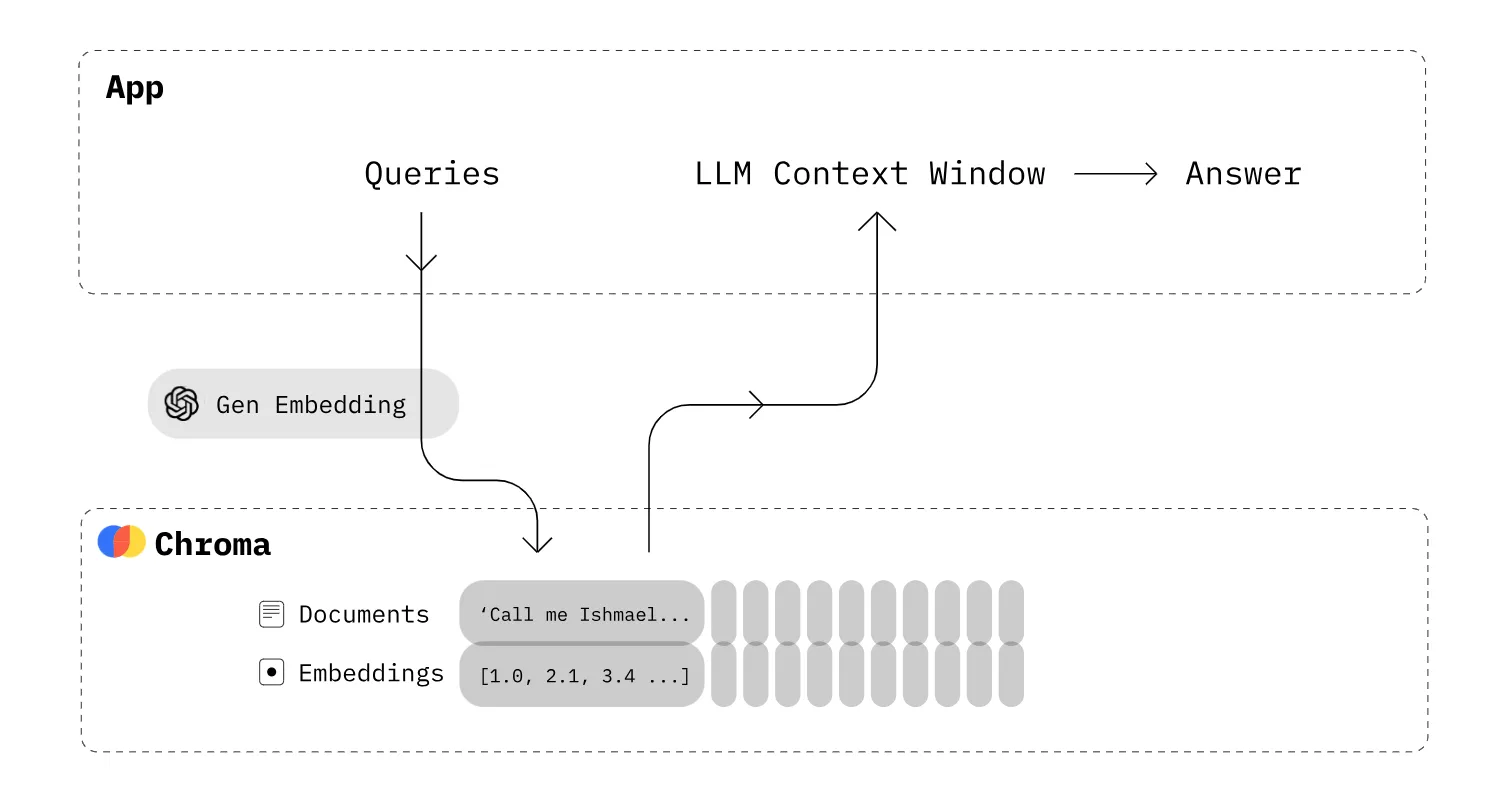
Hình 4: Minh họa việc sửdụng r database Chroma đểtruy vấn các tài liệu có liên quan làm context trong prompt. Ảnh: .
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
9
1 from typing import Union
2 from langchain_chroma import Chroma
3 from langchain_community .vectorstores import FAISS
4 from langchain_community .embeddings import HuggingFaceEmbeddings
6 class VectorDB:
def init(self ,
documents = None ,
vector_db: Union[Chroma , FAISS] = Chroma ,
embedding = HuggingFaceEmbeddings (),
) -> None:
self.vector_db = vector_db
self.embedding = embedding
self.db = self._build_db(documents)
5
7
8
9
AI VIETNAM (AIO2024) aivietnam.edu.vn
23
24
25
26
27
28
def _build_db(self , documents):
db = self.vector_db. from_documents (documents=documents , embedding=self.embedding) return db
def get_retriever(self ,
search_type: str = “similarity”,
search_kwargs: dict = {“k”: 10}
):
retriever = self.db.as_retriever(search_type=search_type , search_kwargs=search_kwargs) return retriever
17
18
19
20
21
22
II.7. Cập nhật file src/rag/offline_rag.py
Tại file này, ta khai báo class Offline_RAG đểxây dựng một chain vềRAG, bao gồm việc sửdụng retriever lấy context, xây dựng prompt và đưa vào model. Nội dung của file như sau:
19
20
21
22
23
24
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
1 import re
2 from langchain import hub
3 from langchain_core .runnables import RunnablePassthrough
4 from langchain_core .output_parsers import StrOutputParser
6 class Str_OutputParser ( StrOutputParser ):
def init(self) -> None:
super ().init ()
def parse(self , text: str) -> str:
return self.extract_answer(text)
def extract_answer (self ,
text_response: str ,
pattern: str = r”Answer :\s*(.*)”
) -> str:
match = re.search(pattern , text_response , re.DOTALL)
if match:
answer_text = match.group(1).strip ()
return answer_text
else:
return text_response
25 class Offline_RAG:
def init(self , llm) -> None:
self.llm = llm
self.prompt = hub.pull(“rlm/rag -prompt”)
self.str_parser = Str_OutputParser ()
def get_chain(self , retriever):
input_data = {
“context”: retriever | self.format_docs ,
“question”: RunnablePassthrough ()
}
rag_chain = (
5
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
10
AI VIETNAM (AIO2024) aivietnam.edu.vn
41
42
43
44
45
input_data
| self.prompt
| self.llm
| self.str_parser
)
return rag_chain
def format_docs(self , docs):
return “\n\n”.join(doc.page_content for doc in docs)
37
38
39
40
II.8. Cập nhật file src/rag/utils.py
Tại file này, ta khai báo hàm tách phần trảlời của model từcâu prompt (phần bắt đầu từ**“Answer:”**):
10
11
12
7
8
9
1 import re
3 def extract_answer (text_response: str ,
pattern: str = r”Answer :\s*(.*)” ) -> str:
match = re.search(pattern , text_response) if match:
answer_text = match.group(1).strip () return answer_text
else:
return “Answer not found.”
2
4
5
6
II.9. Cập nhật file src/rag/main.py
Tại file này, ta khởi tạo toàn bộcác instance của các class, các hàm mà ta đã khai báo trước đóvà kết nối chúng vào trong một hàm duy nhất gọi là build_rag_chain():
11
12
13 def
14
15
16
17
18
1 from pydantic import BaseModel , Field
3 from src.rag.file_loader import Loader
4 from src.rag.vectorstore import VectorDB
5 from src.rag.offline_rag import Offline_RAG
7 class InputQA(BaseModel):
question: str = Field (…, title=“Question to ask the model”)
10 class OutputQA(BaseModel):
answer: str = Field (…, title=“Answer from the model”)
build_rag_chain (llm , data_dir , data_type):
doc_loaded = Loader(file_type=data_type).load_dir(data_dir , workers=2)
retriever = VectorDB(documents = doc_loaded).get_retriever ()
rag_chain = Offline_RAG(llm).get_chain(retriever)
return rag_chain
2
6
8
9
11
AI VIETNAM (AIO2024) aivietnam.edu.vn
Như vậy, ta đã hoàn thiện toàn bộcác code cần thiết đểxây dựng một ứng dụng vềRAG. Đểtổng quát hóa toàn bộquy trình, chúng ta có thểtham khảo qua ảnh sau:
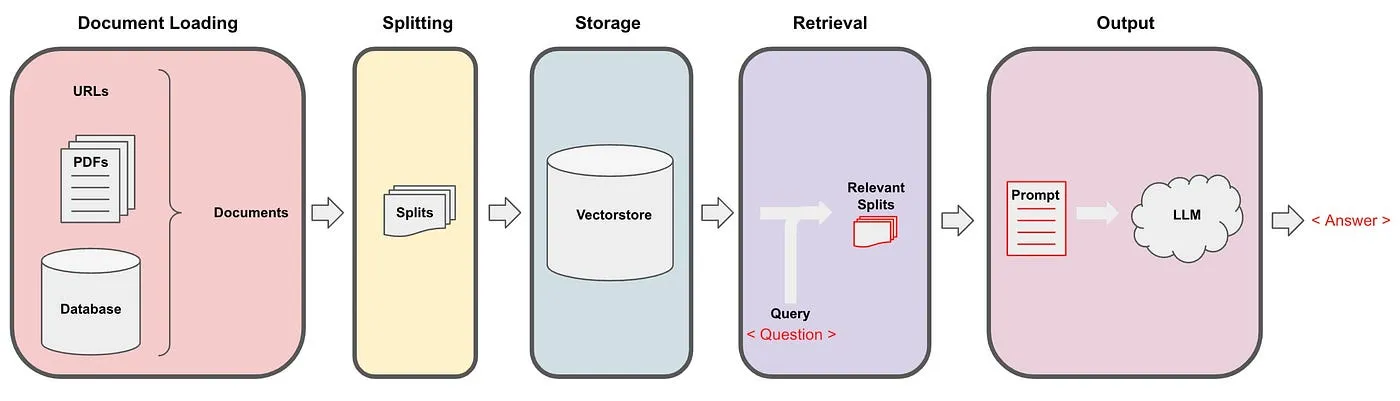
Hình 5: Minh họa chuỗi (chain) các bước xây dựng RAG trong LangChain. Ảnh: .
II.10. Cập nhật file src/app.py
Cuối cùng, ta tạo file dùng đểkhai báo API với LangServe đểtriển khai ứng dụng RAG. Đối với LangServe, cách sửdụng gần như tương tựvới việc sửdụng FastAPI. Nội dung file code nhưsau:
16
18
20
22
23
24
25 )
26
28
29
1 import os
2 os.environ[” TOKENIZERS_PARALLELISM ”] = “false”
4 from fastapi import FastAPI
5 from fastapi.middleware.cors import CORSMiddleware
7 from langserve import add_routes
9 from src.base.llm_model import get_hf_llm
10 from src.rag.main import build_rag_chain , InputQA , OutputQA
12 llm = get_hf_llm(temperature=0.9)
13 genai_docs = ”./ data_source/generative_ai”
15 # --------- Chains ----------------
17 genai_chain = build_rag_chain (llm , data_dir=genai_docs , data_type=“pdf”)
19 # --------- App - FastAPI ----------------
21 app = FastAPI(
title=“LangChain Server”,
version=“1.0”,
description=“A simple api server using Langchain ’s Runnable interfaces”,
27 app. add_middleware (
CORSMiddleware ,
allow_origins =[”*”],
3
6
8
11
14
12
AI VIETNAM (AIO2024) aivietnam.edu.vn
41
44
45
46
49
50
51
allow_credentials =True ,
allow_methods =[”*”],
allow_headers =[”*”],
expose_headers =[”*”],
36 # --------- Routes - FastAPI ----------------
38 @app.get(“/check”)
39 async def check ():
return {“status”: “ok”}
42 @app.post(“/generative_ai”, response_model =OutputQA) 43 async def generative_ai(inputs: InputQA):
answer = genai_chain.invoke(inputs.question) return {“answer”: answer}
47 # --------- Langserve Routes - Playground *----------------*48 add_routes(app ,
genai_chain ,
playground_type=“default”,
path=“/generative_ai”)
30
31
32
33
34 )
35
37
40
Đểkhởi động API, chúng ta duy chuyển đến thư mục root của source code trong terminal (trong trường hợp của bài viết sẽlà thư mục rag_langchain/), sửdụng lệnh sau (sau khi đã cài đặt các thư viện cần thiết cũng như vector database). Lưu ý, nếu bịlỗi do port đã được sửdụng trong máy của bạn thì có thểthay đổi sang một port khác:
1 uvicorn src.app
13
AI VIETNAM (AIO2024) aivietnam.edu.vn
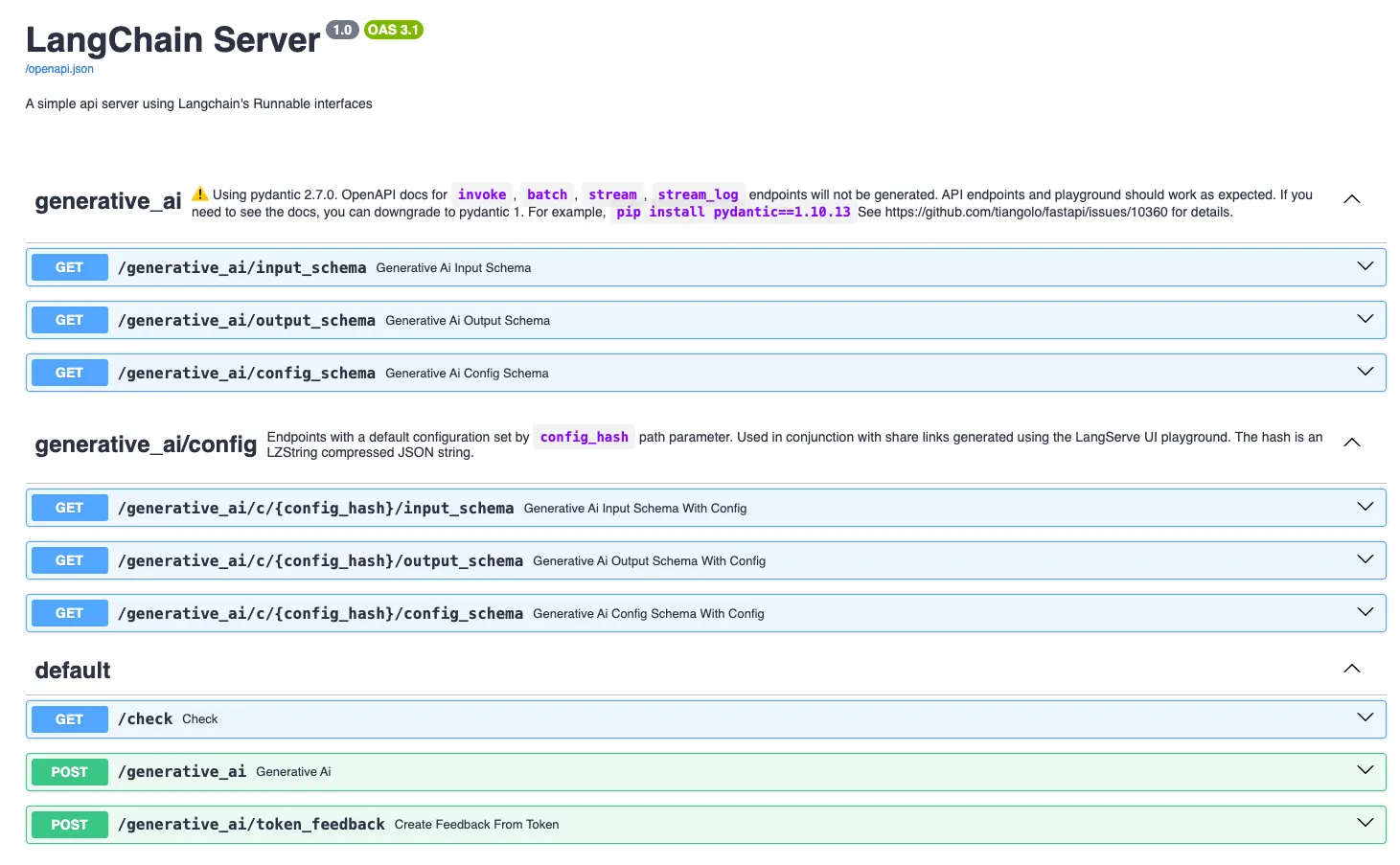
Hình 6: Minh họa API sau khi ta triển khai thành công.
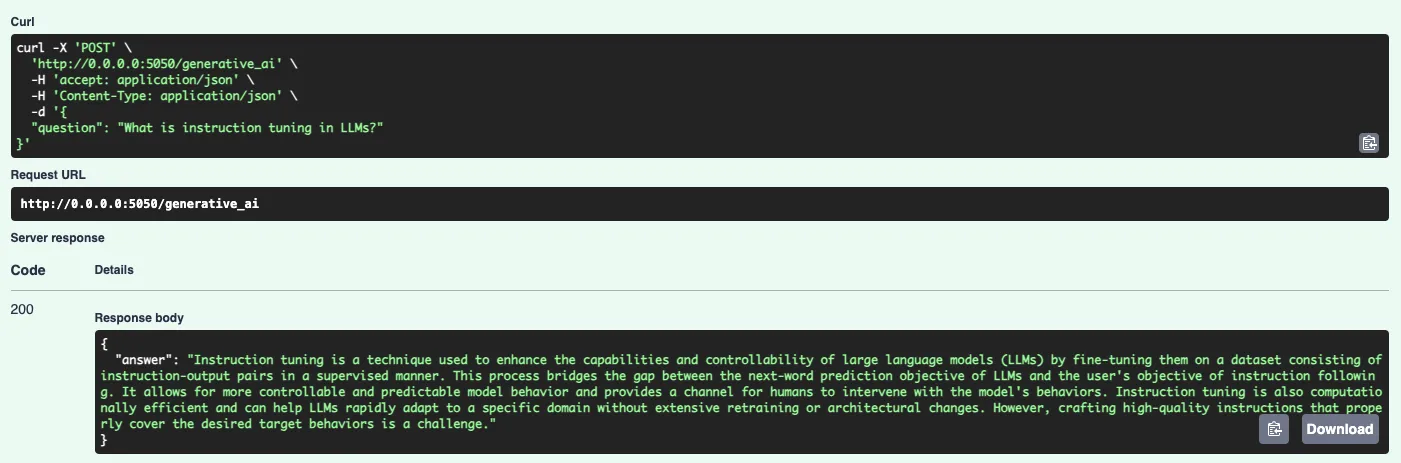
Hình 7: Minh họa một kết quảcủa model thông qua API mà chúng ta đã xây dựng.
14
AI VIETNAM (AIO2024) aivietnam.edu.vn
III. Câu hỏi trắc nghiệm
- LangChain được sửdụng nhằm mục đích gì?
(a) Web Scraping.
(b) Model Quantization.
(c) Building language model-powered applications. (d) Database Management.
- Nội dung nào dưới đây là một thành phần cốt lõi của LangChain? (a) Transformers.
(b) Agents.
(c) Callbacks.
(d) Hooks.
- Trong LangChain, mục đích trong việc sửdụng PromptTemplate là?
(a) Tạo các trường thông tin trong hệcơ sởdữliệu lưu thông tin người dùng. (b) Định nghĩa các tính năng trong giao diện của người dùng.
(c) Tối ưu tốc độxửlý của mô hình.
(d) Chuẩn hóa một cấu trúc phản hồi nhất quán từmô hình.
- Xét đoạn code dưới đây:
3
1 from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
2 from langchain_openai import OpenAI
4 llm = OpenAI ()
5 chat_model = ChatOpenAI(model=“gpt -3.5-turbo -0125”)
Ý nghĩa của đoạn code trên là?
(a) Khởi tạo model GPT 3.5 Turbo-0125.
(b) Tải pre-trained model GPT 3.5 Turbo-0125.
(c) Kiểm tra tốc độđường truyền với ChatGPT API. (d) Các đáp án trên đều sai.
- Ý nghĩa của phương thức from_template() trong class PromptTemplate là? (a) Đểkhởi tạo prompt template từmột file.
(b) Đểkhởi tạo prompt template từmột string.
(c) Đểkhởi tạo prompt template từmột danh sách các tin nhắn. (d) Đểkhởi tạo prompt template từmột prompt template có sẵn.
15
AI VIETNAM (AIO2024) aivietnam.edu.vn
- Trong LangChain, loại OutputParser nào dưới đây có thểđược sửdụng đểtrảvềkết quảcủa mô hình dưới dạng JSON?
(a) PydanticOutputParser.
(b) RegexOutputParser.
(c) JsonOutputParser.
(d) YamlOutputParser.
- Xét đoạn code dưới đây:
10 )
11
13
14 )
15
17
1 from langchain import HuggingFaceHub
2 from langchain import PromptTemplate
4 template = """ Question: {question}
6 Answer: """
7 prompt = PromptTemplate(
template=template ,
input_variables =[’question ’]
12 hub_llm = HuggingFaceHub(
repo_id=’google/flan -t5 -xl’
16 llm_chain = prompt | hub_llm
18 print(llm_chain.run(“What year was the World Cup first held?”))
3
5
8
9
Ý nghĩa của các dòng code 16 là gì?
(a) Khai báo hệcơ sởdữliệu vector.
(b) Khởi tạo LLMChain với LLM và Prompt. (c) Cài đặt ủy quyền và bảo mật cho người dùng. (d) Phân tích và trực quan hóa dữliệu.
- Xét đoạn code dưới đây:
4
1 from langchain_community . document_loaders import PyPDFLoader
3 pdf_loader = PyPDFLoader(url , extract_images =True)
5 docs = pdf_loader.load ()
2
Tham sốextract_images tại dòng code 3 có chức năng gì? (a) Trảvềtất cảảnh từfile pdf.
(b) Bỏqua ảnh, chỉload text.
(c) Phân tích ảnh thành vector.
(d) Chuyển đổi ảnh trong file pdf thành text.
16
AI VIETNAM (AIO2024) aivietnam.edu.vn
- Tại sao chúng ta cần phải chia nhỏcác tài liệu đầu vào thành các tài liệu ngắn hơn? Chọn câu trảlời SAI.
(a) Giúp LLM tập trung tạo ra câu trảlời chỉdựa trên các thông tin có liên quan. (b) Tiết kiệm bộnhớcho phần cứng.
(c) Chỉdựa vào một phần nhỏtài liệu thì mô hình vẫn trảlời chính xác.
(d) Giúp mô hình LLM chạy nhanh hơn.
- Xét đoạn code dưới đây:
14
15
16 )
18
21
1 from langchain_community . document_loaders import PyPDFLoader
2 from langchain_text_splitters import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
3 from langchain_community .embeddings import HuggingFaceEmbeddings
4 from langchain_chroma import Chroma
6 pdf_url = “https :// arxiv.org/pdf/2401.18059v1.pdf”
8 # PDF loader
9 pdf_loader = PyPDFLoader(pdf_url , extract_images =True)
10 pdf_pages = pdf_loader.load ()
12 # Splitter
13 splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter (
chunk_size=300 ,
chunk_overlap=0,
17 docs = splitter. split_documents (pdf_pages)
19 # Embedding model
20 embedding_model = HuggingFaceEmbeddings ()
22 # vector store
23 chroma_db = Chroma.from_documents(docs , embedding= embedding_model )
5
7
11
Nhiệm vụcủa embedding_model là gì?
(a) Dùng biến đổi chuỗi đầu vào thành các vector cho cơ sởdữliệu vector. (b) Dùng đểlập chỉmục cho cơ sởdữliệu.
(c) Dùng đểtìm kiếm tài liệu.
(d) Dùng đểtính toán độtương đồng.
17
AI VIETNAM (AIO2024) aivietnam.edu.vn
IV. Phụlục
-
Datasets: Các file dataset được đềcập trong bài có thểđược tải tại .
-
Hint: Các file code gợi ý có thểđược tải tại .
-
Solution: Cile code cài đặt hoàn chỉnh và phần trảlời nội dung trắc nghiệm có thểđược tải tại (Lưu ý: Sáng thứ3 khi hết deadline phần nội dung này, ad mới copy các tài liệu bài giải nêu trên vào đường dẫn).
-
Demo: Web demo và mã nguồn của ứng dụng có thểđược truy cập tại .
-
Rubric:
| Mục | Kiến Thức | Đánh Giá |
|---|---|---|
| I. | - Kiến thức vềmô hình ngôn ngữlớn (LLMs). |
- Kiến thức bài toán Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG). | - Hiểu được các nội dung cơ bản vềLLMs và RAG. Input Output của bài toán RAG và luồng xửlý cơ bản. | | II. | - Các kiến thức cơ bản vềthư viện LangChain.
- Tổng quan các cách bước cơ bản trong việc sửdụng LangChain.
- Chức năng một sốhàm cơ bản trong LangChain nhằm phục cho cài đặt ứng dụng RAG.
- Khái niệm vềAPI và luồng triển khai API cơ bản. | - Nắm được các nội dung và chức năng cơ bản của thư viện LangChain.
- Có thểsửdụng thư viện LangChainđểcài đặt một ứng dụng RAG sửdụng LLMs. |
- Hết -
18